Remember when everything was Intranet focused? It seemed right at that time when all enterprise activity was internal, behind the Firewall, but in reality it was an early development stage in moving to external Internet based activities cumulating in Digital Business. Right now IOT looks to be at the same stage in many enterprises, so it’s the right time to start to understand the bigger picture as well, otherwise todays’ relatively small deployments could be tomorrow’s problem.
Research report now available: The Foundational Elements for the Internet of Things (IoT)
Designing IOT solutions has to, by its very nature, involve networks, but the challenge is that IOT devices are ‘small’ and ‘distributed’, in comparison to conventional networked items such as PCs, Servers, or even Mobility devices. The design of an IoT solution network needs to be approached differently.
The ‘Internet of Everything’ is a Cisco term used to deliberately identify that with the lowering of processor prices, and the rise in ‘consumer’ style devices of all sorts. As demonstrated at Consumer Electronic Show this year, and other trade shows, a huge range of devices are expecting to connect and interact through the Network. The future, which is arriving now, requires not just massively expanded networking capabilities, but a wholly different architecture to cope. An Enterprise might start with an internal deployment of IoT connected to its internal network, as an ‘Intranet of Things’ solution, it will soon as with all Internet based services rapidly expand to embrace external and ‘everything’.
Digital Business means that all Enterprises initial ‘controlled’ Digital Business external activities focusing on sales and purchasing will, as the overall market inevitably changes, will expand. An Enterprise will have to ‘participate’ in the massively connected ‘Internet of Everything’ environment of the Digital Society to gain information, spot opportunities and organize responses.
At the Network level this is part of the fundamental shift already underway. A shift from resource centric (Cloud) based data centers supporting interconnected centralized internal IT networks towards de-centralized networks of small-distributed devices. This introduces a shift in data traffic patterns, as much of the new IOT traffic will remain ‘local’ and with no obvious pattern. This change is fundamental enough to require the network technology architecture to have to change and to need a whole new lexicon of terms.
The diagram below illustrates on the left the usual visualization of a legacy IT network, frequently referred to as ‘tree and branch’ architecture, with the main data flows running to a centralized Data center, or master server. Interconnection with other external Internet resources are, ideally, from the IT security point of view made through well-managed gateways at the Data Centre. The term ‘north-south’ is used to describe the data flows in Tree and Branch architecture which are usually predictable, and manageable.
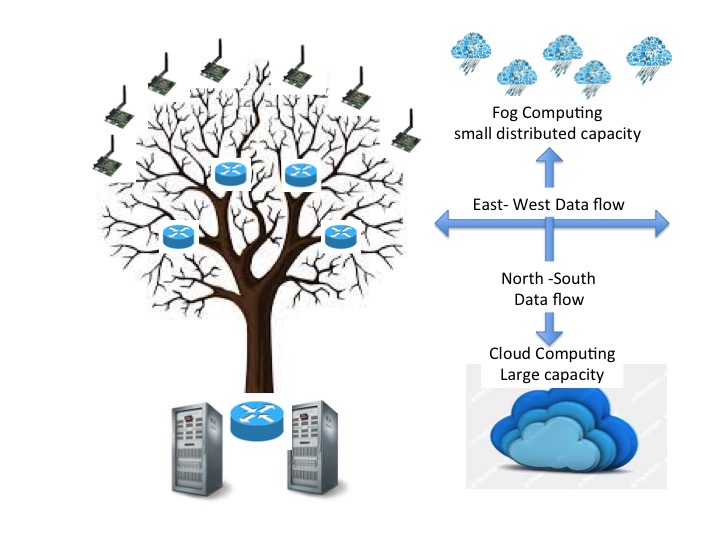
Its difficult diagrammatically to illustrate in such a neat manner the mass connected environment that IoT and Internet of Everything will introduce. The right hand illustration is a simplistic representation mainly to introduce where the various terminologies apply. Here the term North-South continues to describe conventional data flows to and from a centralized set of resources, but introduces the term East-West to describes data flows between the huge number of distributed devices that are networked.
In time East-West (or around the edge) data flows are expected to become dominant as cheap processor power and the sheer number of Devices expected to participate in ‘Smart Sessions’ will out number the more restricted functionality of conventional IT style PCs working in Client-Server Enterprise Applications inside an Enterprise.
The sharp eyed will also have spotted the addition of the term ‘Fog Computing’ to describe the new architecture in which all these IoT, and IoE, smart devices operate creating the East-West data flows. Cloud Computing by contrast supports the architecture that provides large conventional large Data Center resources in the North-South IT architecture.
The term, ‘Fog’, is used by Meteorologists to describe a low level, close to ground, wide spread effect produced by the same conditions that produce Clouds high in the sky. Clouds are generally though of as being more distinctly separate entities whereas Fog swirls round and covers large areas at ground level. As such Fog makes sense as a term to be used for de centralized thin spread computing in contrast to Cloud for the defined centralized computing model. Cisco first introduced the term, but its use has spread, and become increasingly defined as a key part of the architecture required. As an example in the diagram below;
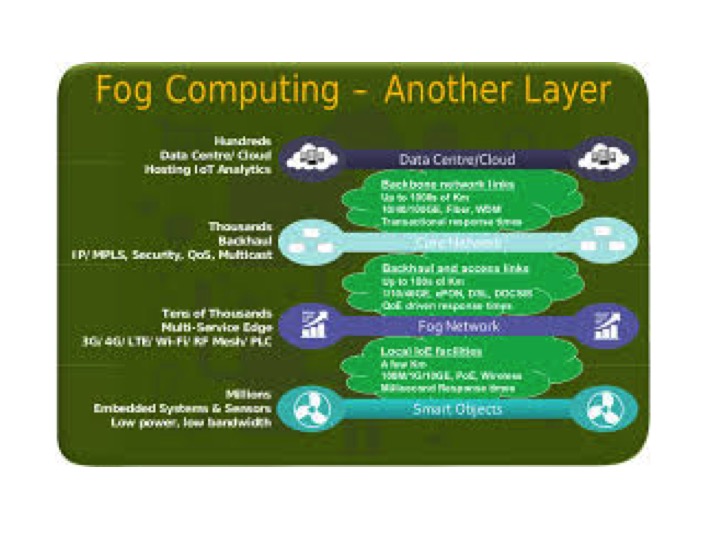
Source; http://thoughtsoncloud.com/2014/08/fog-computing/
IoT is all about Data of course, so how the data environment is made to function is clearly the next question. Cisco also use the term ‘taking the query to the data’ when talking about Fog Computing. This causes more than a little confusion, especially when considering the excellent capabilities of Salesforce and SAP IoT solutions. (Indeed it’s the question of what and how to use the data that defines the differences in the SAP and Salesforce approaches to IoT).
The data from ten IoT devices is easy to handle and use, the data from one hundred devices less so, and the data from a thousand small IoT devices is a flood of small data packets that are extremely difficult to handle. Fog Computing architecture sees local consolidation and processing as one of its main duties.
However, there are three main data flows will usually result in a ‘forward’ of the locally processed data across the network as consolidated data for enterprise processing; 1) a trigger alert condition occurs in the local group; 2) at set times, or intervals, updates are forwarded; or 3) a query is received requesting certain data at that moment.
In IoT solutions, even at the smaller Intranet scale and, without moving to the scaled up adoption of Fog Computing architecture, the whole topic of ‘networking’ data flows is an important consideration. With time, as with the adoption of Client-Server architecture and IP based networking in the past, it will become recognized as a critical success factor in IOT/IoE solutions. Some experienced IoT solution architects even think the Network will function as the new Middleware.
The next post in this series will examine the role of the Network as an Orchestrator of data flows within Virtual networks created by a Query or Event.
Resources
The Foundational Elements for the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Elements of Business Architecture for Digital Transformation
Boards Prepare Executives for Digital Business and Digital Leadership





