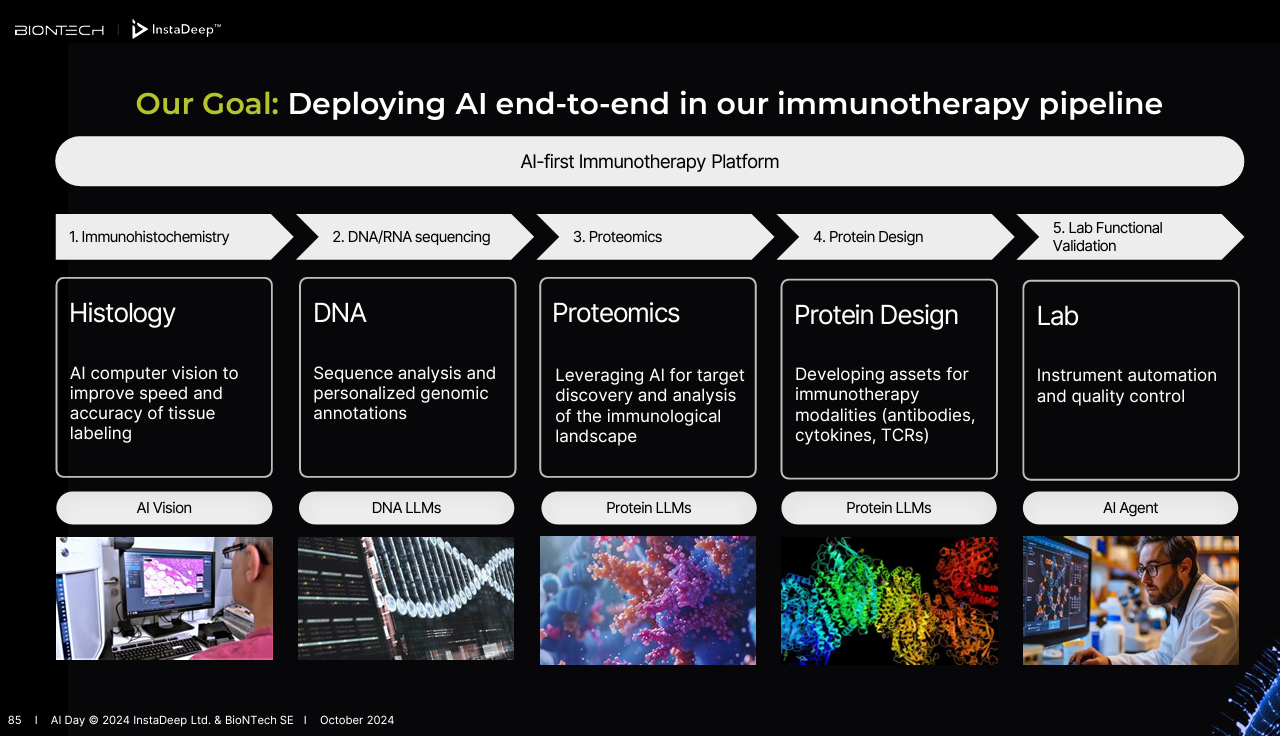
BioNtech's InstaDeep, which was acquired in 2023 for about $682 million, has released a series of foundational generative AI models for proteins and DNA and released them on its DeepChain platform and outlined a supercluster called Kyber.
The news, outlined at BioNtech's AI innovation day, highlights how foundational models are branching out into industry specific use cases. In BioNtech's case, its InstaDeep unit is looking to embed AI throughout the life sciences, R&D and drug discovery value chain.
InstaDeep has even created an AI-driven lab agent built on its proprietary data and Meta's Llama family of models.
BioNtech in recent years has been best known for its COVID-19 vaccine partnership with Pfizer. However, BioNtech historically focused on mRNA cancer treatments. BioNtech is betting that AI can drive its drug pipeline for years to come with its acquisition of InstaDeep, which counted Google as an investor. BioNtech and InstaDeep formed a joint AI lab in 2020 and the partnership quickly accelerated.
Ugur Sahin, CEO BioNTech, explained the company's bet on InstaDeep, which also has its own supercomputing cluster called Kyber. Kyber is coming online in Paris and enables InstaDeep to train its own foundational models without the cost and queue involved with cloud computing.
Sahin said:
"Every cancer treatment for every patient is a new battle. Every cancer cell is different. How can we develop treatments that address tumor cells? Cancer is evolving. Cancer is adaptable. This has now become a high-level computational question."
Sahin added that cancer treatment in the future will start with clinical samples from the patient and an analysis of genetic changes in tumor cells that will generate about 4 terabytes of data for each patient. "We need AI, machine learning and algorithms to come to the right conclusions," he said. "AI gives us the opportunity to do that at a much deeper and faster scale."
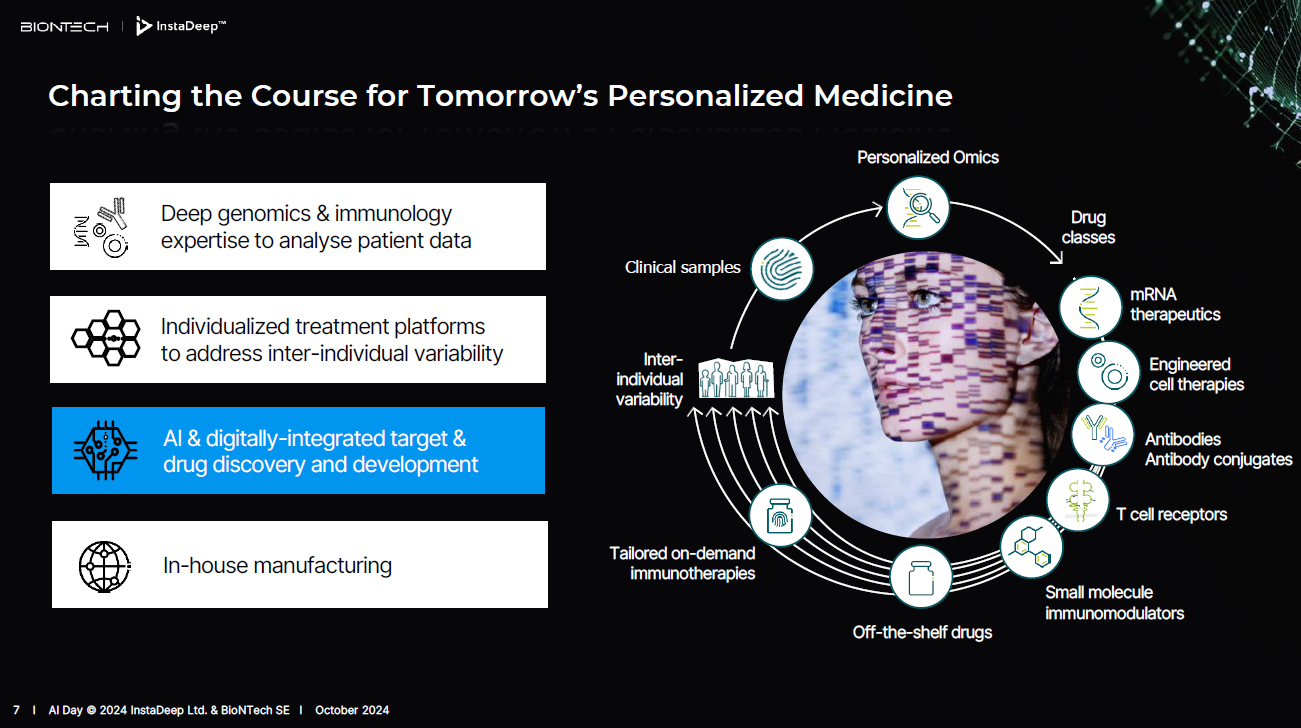
Is BioNtech a biotech company or an AI company? Both. Life sciences and AI are likely to become symbiotic.
Ryan Richardson, Chief Strategy Officer at BioNTech, said the company is looking to build an "AI personalized immunotherapy platform." The value drivers for the InstaDeep purchase revolved around cost efficiencies from internalizing model training, building foundational models for vaccines and therapeutics and applying AI to drug discovery.
"The primary use case is to embed AI in drug discovery with the ability to combine our therapeutic platforms on one hand, which are very novel, and the AI capabilities that InstaDeep brings to bear," said Richardson. "There is truly profound disruptive potential in terms of developing or discovering new drugs."
- AI 15O's Matt Lewis on GenAI adoption, psychology and life sciences
- Welldoc Chief AI Officer Anand Iyer on AI, data and healthcare transformation
Karim Beguir, CEO and Co-Founder of InstaDeep, said the goal is to work with BioNtech closely to become "a leader in digital biology." Beguir added that for InstaDeep and BioNtech to lead in digital biology his company also needs to be a leader in AI. "The same technology can apply to multiple use cases," said Beguir. "We are leaders in industrial optimization within biology and outside of biology these add up together. The objective is to continue to be a leading power in the world of AI."
Here's a look at what InstaDeep is working on as part of BioNtech.
A supercomputing cluster named Kyber. Beguir said the Kyber supercluster is built on 224 Nvidia H100 GPUs, 86,000 CPU cores, 1.7 petabytes of persistent storage and 400 Gbps RoCE network. The cluster, built on-premises with Dell, totals about 0.5 ExaFLOPs and is one of the top 20 H100 GPU clusters globally.
"We are now able to take all the work that we have built upon over the last several years and scale it up over the next five, six, seven, 10 years," said Beguir.
InstaDeep uses an in-house rack design that's easy to expand with modular nodes that offer consistent performance, cost, power and cooling. Standard designs will minimize costs over time. InstaDeep also tailored its AI software stack to its workloads with open standards.

Beguir said InstaDeep built the supercluster to avoid vendor lock-in and benefit from predictable costs while scaling models. Kyber enabled InstaDeep to train genAI models with more than 15 billion parameters with hardware efficiency on part with the latest Meta Llama 3.1 foundational model.
Bayesian Flow Networks (BFNs), a new class of generative model that uses Bayesian inference to update beliefs about data. BFNs generate discrete data in a continuous way and are better suited for proteomics and modeling protein folding, function prediction, antibody design and sequence generation.
InstaDeep wants to use BFNs to build foundational models based on heterogeneous scientific data to give scientists more flexibility. A model called AbBFN-X is designed to be a multimodal model for antimodels with 26 different attributes jointly modeled.
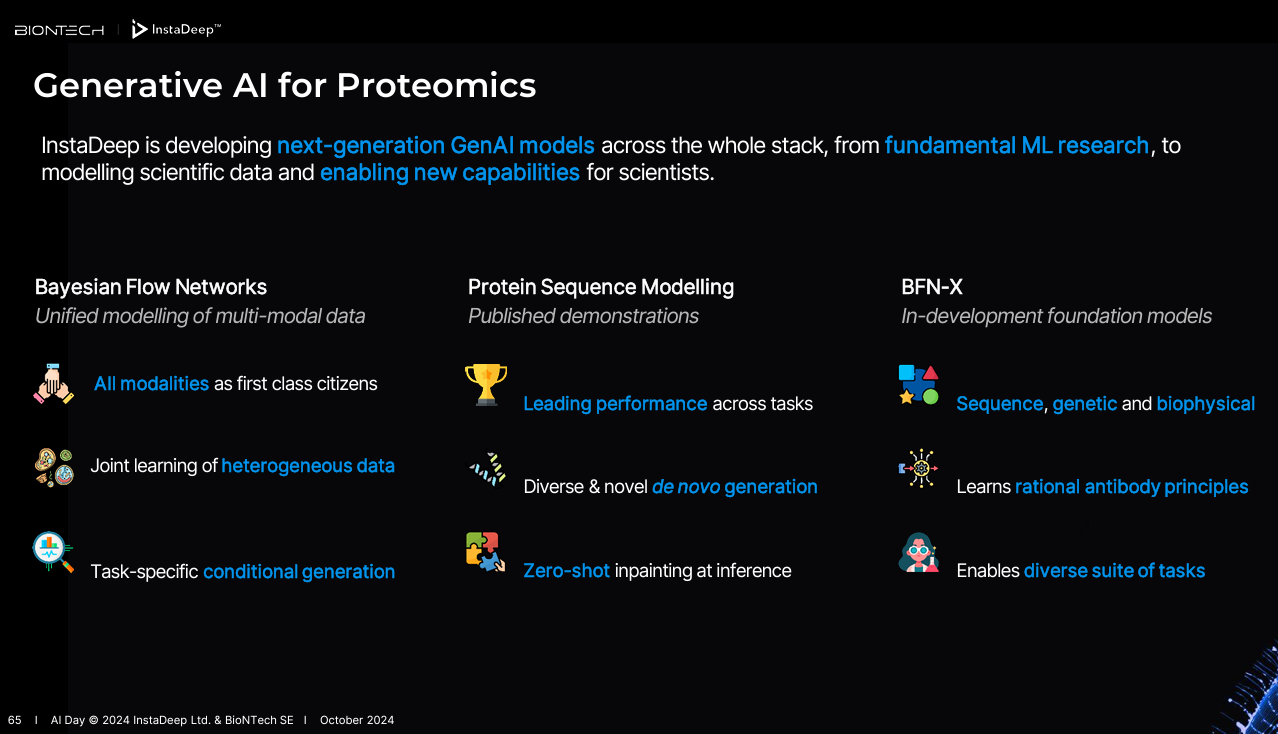
DeepChain, a platform designed to use AI to accelerate the R&D pipeline, gains new features. DeepChain is getting generative protein models, ProtBFN and AbBFN, and foundational models for DNA, Nucleotide Transformer and SegmentNT. These models, which can be customized and fine-tuned, are available on Hugging Face under the genomics tag.

- Enterprises leading with AI plan next genAI, agentic AI phases
- 13 artificial intelligence takeaways from Constellation Research’s AI Forum
Laila AI agents built on Meta Llama 3.1. Laila is integrated throughout the DeepChain platform and can recommend models and analyze data with internal and external tools. Laila can also visualize results, plot data and zoom in on certain DNA sequences and positions.
InstaDeep executives said that Laila, which comes in multiple sizes, is more than a chat bot and can use its expert knowledge of biology to reason, make decisions and provide feedback.
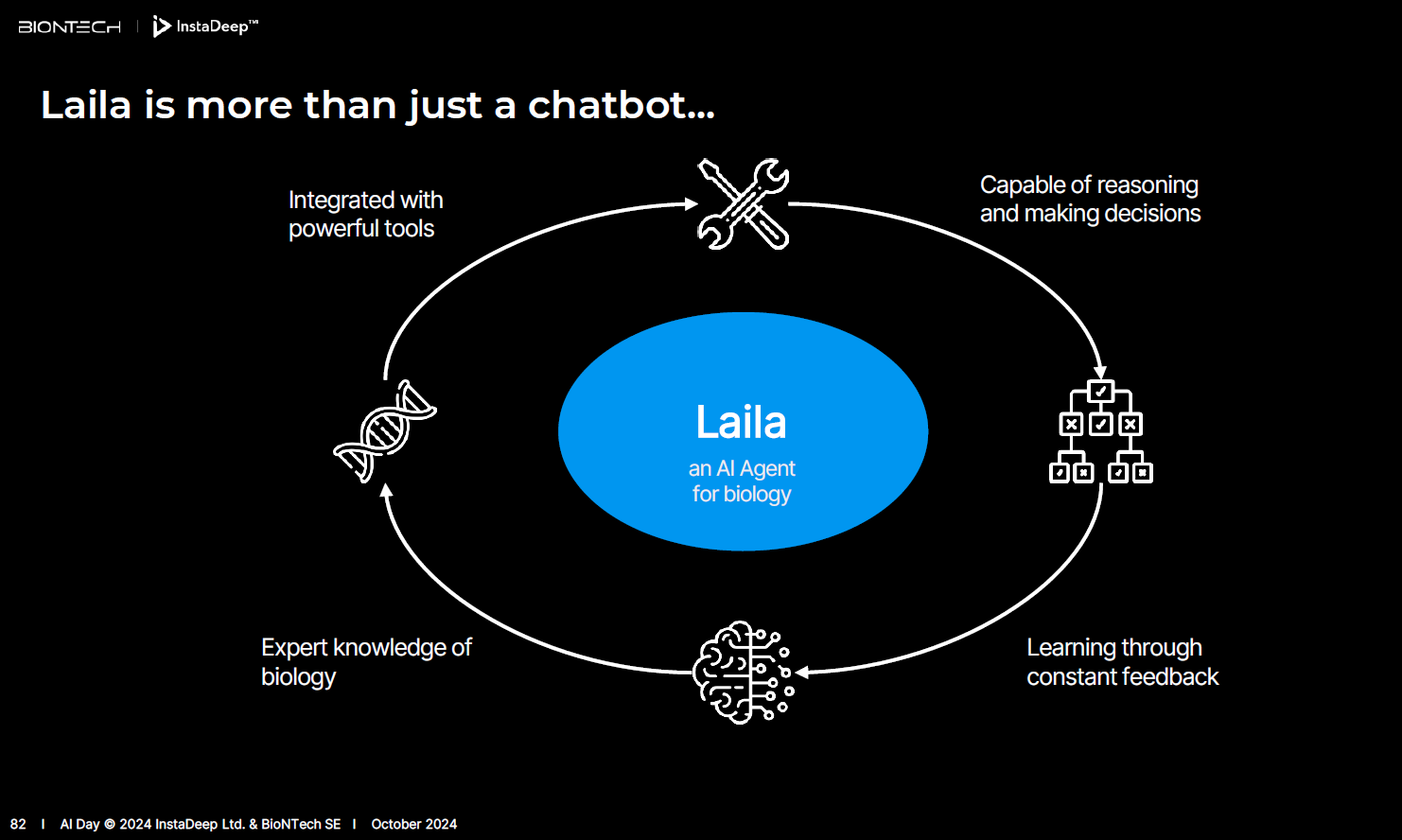
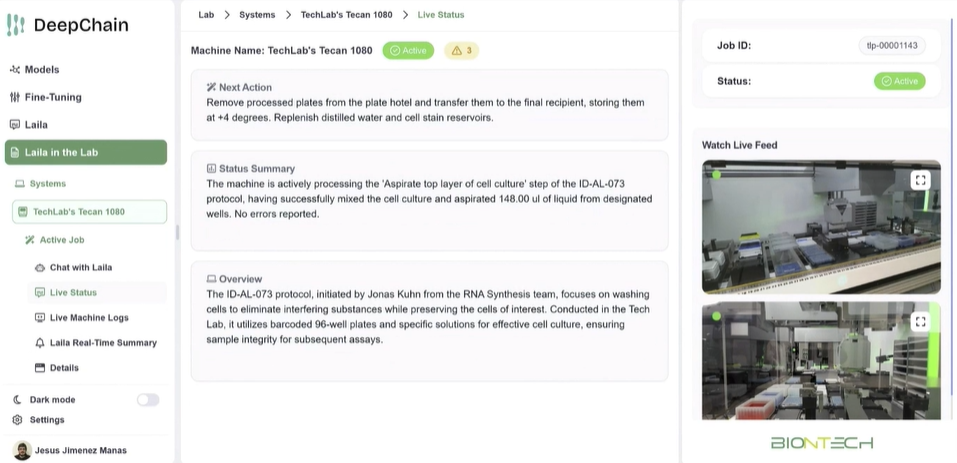
The company is also working to leverage its models across scientific and R&D workflows. InstaDeep has designed AI tools to automate labs, annotate tissue, segment pathology images and identify novel therapeutic targets.
Constellation Research analyst Holger Mueller said:
"While most of the CxO attention is on cloud platforms and AI vendors when it comes for the latest on genAI, there is substantial innovation coming from the biotech industry as well. BioNtech (where the founder would go on vacation with its workstation) acquired its own AI startup and it is showing significant progress on what matters at the moment - the 'uber ai' that chooses the right AI / statistical models for positive outcomes in protein folding, cancer research and more. It's good to see more AI model competition, especially coming from a practitioner."
More:
- Themes from the healthcare data, AI, disruption front lines
- 8 takeaways from Constellation Research's Healthcare Transformation Summit
- Medtronic aims to leverage medical device data for AI-enabled care
- Google Cloud's healthcare push accelerates with Vertex AI, MedLM, Healthcare Data Engine
- CVS Health’s Transformation Rides on Data, AI and Customer Experiences
- AI Meets Mental Health Assessments: How Futures Recovery Healthcare, Aiberry Co-innovated


